I. What is PETG ?
Polyethylene terephthalate glycol, or PETG, is quickly becoming a favored material in the 3D printing community. Known for its robustness and flexibility, PETG offers an appealing blend of properties that make it suitable for a wide range of applications. As the 3D printing industry grows, so does the emphasis on selecting materials that are not only effective but also safe for both users and the environment. This blog post explores PETG in the context of 3D printing, focusing on its safety and emissions compared to other popular materials like PLA and ABS.
♻️ A greener choice
- Recyclable: PETG is a thermoplastic that can be recycled, making it a more environmentally friendly option than other plastics.
- Durability: PETG’s durability and resistance to moisture and chemicals mean that products made from PETG can have a longer lifespan.
- Transparency: PETG’s transparency makes it possible to create clear, transparent products, which can be used in eco-friendly packaging, displays and more.

II. PETG vs PLA: Comparing Safety and Emissions
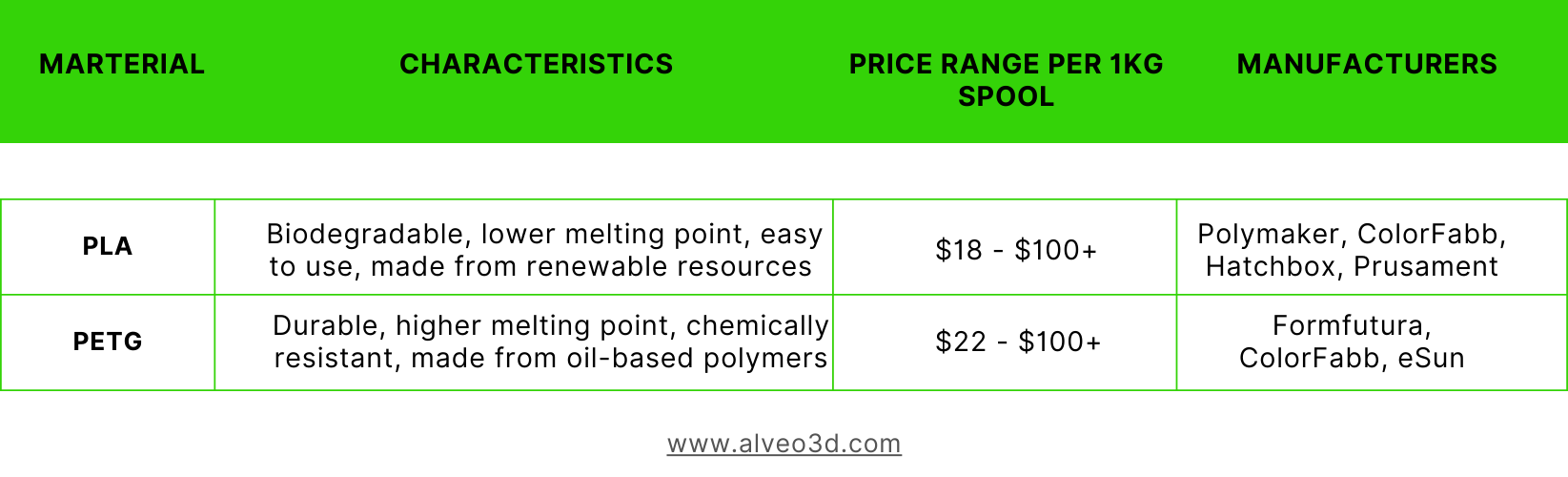
1. Characteristics of PETG and PLA
PETG and Polylactic Acid (PLA) are both thermoplastics widely used in 3D printing, but they differ significantly in their properties and impacts. PLA is known for its ease of use and eco-friendly profile, derived from renewable resources like cornstarch. PETG, on the other hand, offers enhanced durability and thermal resistance, making it a preferred choice for functional parts.
2. Impact on health and environment
When it comes to safety and emissions, both materials have their advantages. Our study in 2021 found that PETG is often highlighted for its lower emission levels during printing. Unlike PLA, which can emit ultrafine particles and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), PETG tends to produce fewer emissions, reducing potential health risks. Insights from Alveo3D suggest adopting safer printing practices, such as using well-ventilated spaces, to further mitigate these risks
PETG vs PLA
3. Advantages of PETG over PLA
PETG stands out for its durability and flexibility, which are critical for many engineering applications. Additionally, its emission levels are generally lower than those of PLA, making it a safer choice for indoor printing environments. This balance of performance and safety underlines the growing preference for PETG among 3D printing enthusiasts and professionals alike.
Here is the comparison for PLA and PETG:
III. PETG vs ABS
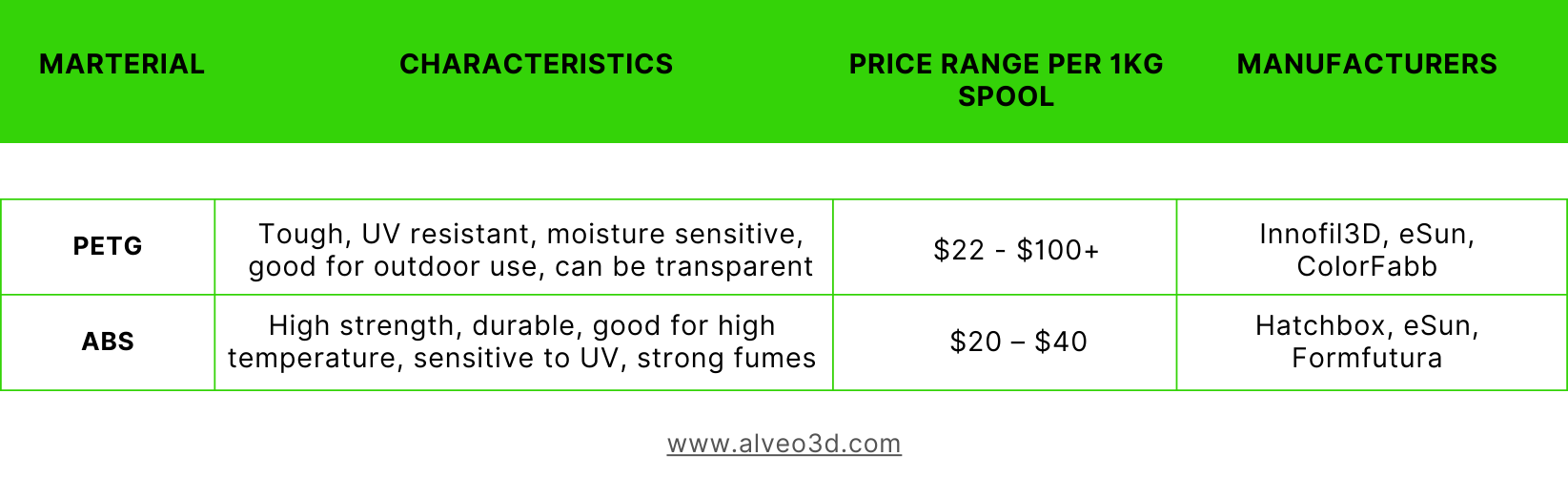
1. PETG and ABS properties
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) has long been a staple in the 3D printing world, prized for its strength and heat resistance. However, ABS is also known for its higher emission rates of styrene, a potential health hazard. PETG offers a compelling alternative, combining similar durability with fewer safety concerns.
2. Emission Comparison and Safety Implications
Our research pointed out that ABS filament emits the most nanoparticles during 3D printing, significantly higher than PLA and PETG, posing a greater health risk in unventilated spaces. PETG’s lower emission rates compared to ABS highlight its appeal as a safer alternative.
PETG vs ABS
3. Why PETG is a Safer to ABS?
PETG’s advantages go beyond its physical properties to encompass safety and environmental considerations. Its lower VOC emissions contribute to a healthier printing environment, minimizing risks to users and offering a greener footprint.
Here is the comparison for PETG vs ABS:
Even though PETG in itself may be considered food-safe, it consists of layers, as every 3D print, in which bacteria can grow over time. You can prevent this by applying a food-safe (epoxy) coating. Also, a stainless-steel nozzle should be used for if food is the intended application.
IV. Solutions for Secure 3D Printing with PETG
Alveo3D has been at the forefront of developing solutions that enhance the safety of 3D printing with PETG. Their enclosures and air filtration systems are designed to minimize users’ exposure to harmful emissions, showcasing their commitment to secure and environmentally responsible printing practices.
PETG’s blend of performance, safety, and lower environmental impact positions it as a material of choice for the future of 3D printing. With companies like Alveo3D leading the way in safety-focused innovations, the community can look forward to advancing the technology with health and sustainability in mind.
We encourage readers to explore Alveo3D’s range of products designed to make 3D printing with PETG not only more efficient but also safer for everyone. Discover how their solutions can enhance your printing projects while prioritizing health and environmental protection.

V. Why we chose PETG over PLA and ABS ?
- Increased Durability: PETG is known for its superior durability compared to PLA. It can withstand higher mechanical stresses, making it ideal for robust functional parts.
- Heat Resistance: It has a higher melting point than PLA, meaning it can withstand higher temperatures without deforming. This makes it suitable for applications requiring some heat resistance.
- Chemical Resistance: It’s resistant to many chemicals, making it a wise choice for environments where it may be exposed to solvents or aggressive chemicals.
- Lower Fine Particle Emissions: According to our emission analysis, PETG generally emits fewer nanoparticles than ABS, making it a safer option in terms of potentially harmful emissions.
- Color Options: available in a variety of colors, including transparent versions, providing greater design flexibility.
- Environmental Considerations: While PLA is biodegradable and made from renewable resources, PETG is derived from oil-based polymers. However, PETG can be recycled, reducing its environmental impact.
FAQ
1. How to print PETG ?
To print with PETG, ensure your 3D printer’s bed is clean and leveled. Preheat the bed to around 70-80°C and the extruder to 230-250°C. Apply an adhesive, like glue stick or hairspray, to the bed to improve first layer adhesion. Print at a slower speed for the first layer to ensure it sticks well. Adjust the print speed and temperature based on your printer’s capabilities and the filament manufacturer’s recommendations. Always print in a well-ventilated area due to PETG’s potential to release fumes.
2. Is PLA stronger than PETG ?
PETG is generally considered stronger and more durable than PLA. It has higher heat resistance, better flexibility, and is less prone to breaking under stress. PLA, while sturdy in its own right and easier to print with, is more brittle and susceptible to degrading over time, especially under high heat or UV exposure. Therefore, for applications requiring more strength and durability, It’s often the preferred choice.
3. Can we laser cut PETG ?
Yes, you can laser cut PETG, but it requires careful handling due to its sensitivity to heat. PETG can be cut with a laser cutter; however, achieving clean edges might require experimenting with laser power and cutting speed settings to avoid melting or warping the material. It’s essential to use proper ventilation as cutting PETG can release fumes. Always consult the laser cutter’s manual and safety guidelines specific to PETG to ensure optimal results and safety during the process.
4. Is PETG toxic to print ?
Printing with PETG is generally considered safe, especially when compared to materials like ABS. PETG emits fewer harmful particles and odors during printing. However, it’s still recommended to print in a well-ventilated area to minimize any potential exposure to fumes.
Beside of that, using a HEPA filter or an enclosure with a filtration system can significantly reduce emissions and improve air quality when printing with PETG or any other filament. These measures are especially beneficial in enclosed spaces, helping to capture fine particles and potentially harmful gases, ensuring a safer printing environment.
5. Is PETG filament food safe ?
Yes, PETG filament is considered food-safe. Due to its chemical composition, which is similar to PET (polyethylene terephthalate), PETG is generally recognized as safe for contact with food by regulatory authorities like the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) in the United States.
This makes PETG a suitable choice for 3D printing objects that will come into contact with food, such as kitchenware, utensils, and food containers. However, it’s essential to ensure that the 3D printing process and the filament used meet food safety standards and are free from contaminants. Additionally, proper cleaning and maintenance of printed food-safe items are recommended to ensure their safety.